The integrated current sensing chip consists of a high-performance Hall sensing core, internal conditioning circuitry, and a magnetic circuit structure, with an output voltage proportional to the test current
Ordinary silicon (Si) Hall elements and matrix compound semiconductor Hall elements both have the function of "detecting magnetic fields", but their properties are very different. Under the same voltage, the output voltage of Hall element has a great relationship with its material, and the matrix of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and indium antimonide (InSb) are ideal materials for the core of Hall magnetic sensing.

Perspective view of the integrated current sensing chip

Product diagram of the integrated current sensor chip
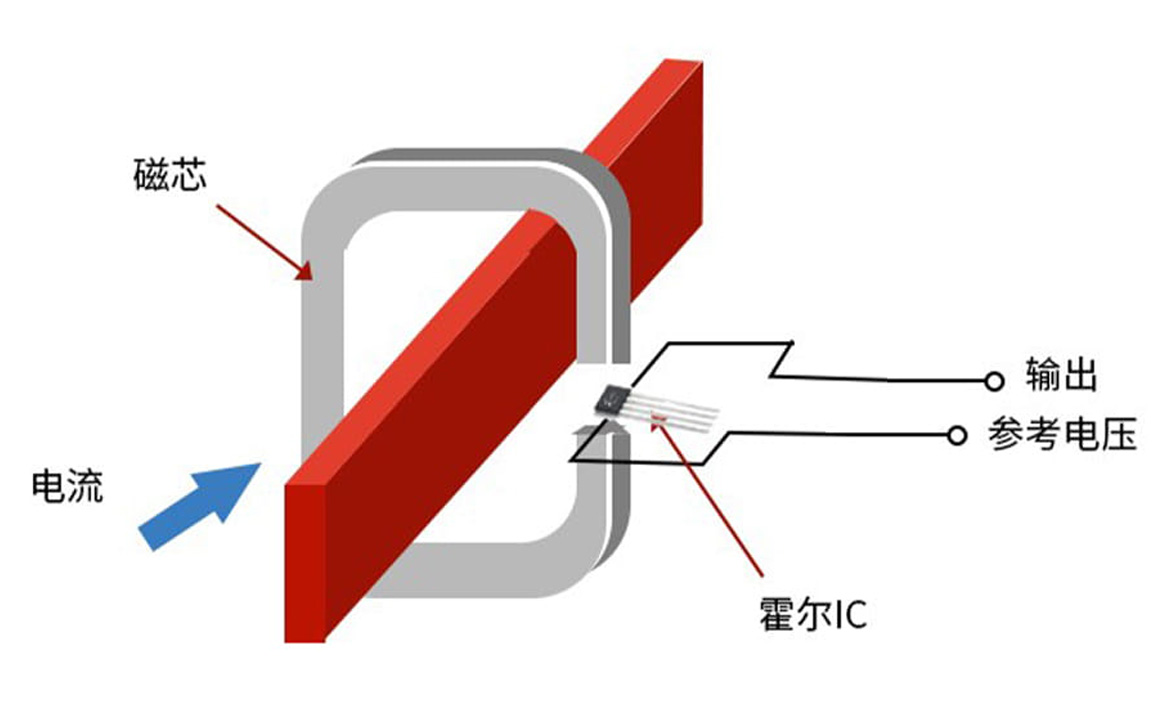
Schematic diagram of an integrated current sensing chip
| Model | Image | Installation | Operating Voltage (V) |
Measuring range (A) |
Precision (@T=25℃) |
Insulation withstand voltage (V) |
Bandwidth (Hz) |
Response Time (us) |
Operating Temperature (℃) |
Primary on-internal resistance (mΩ) |
Form factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC182 |
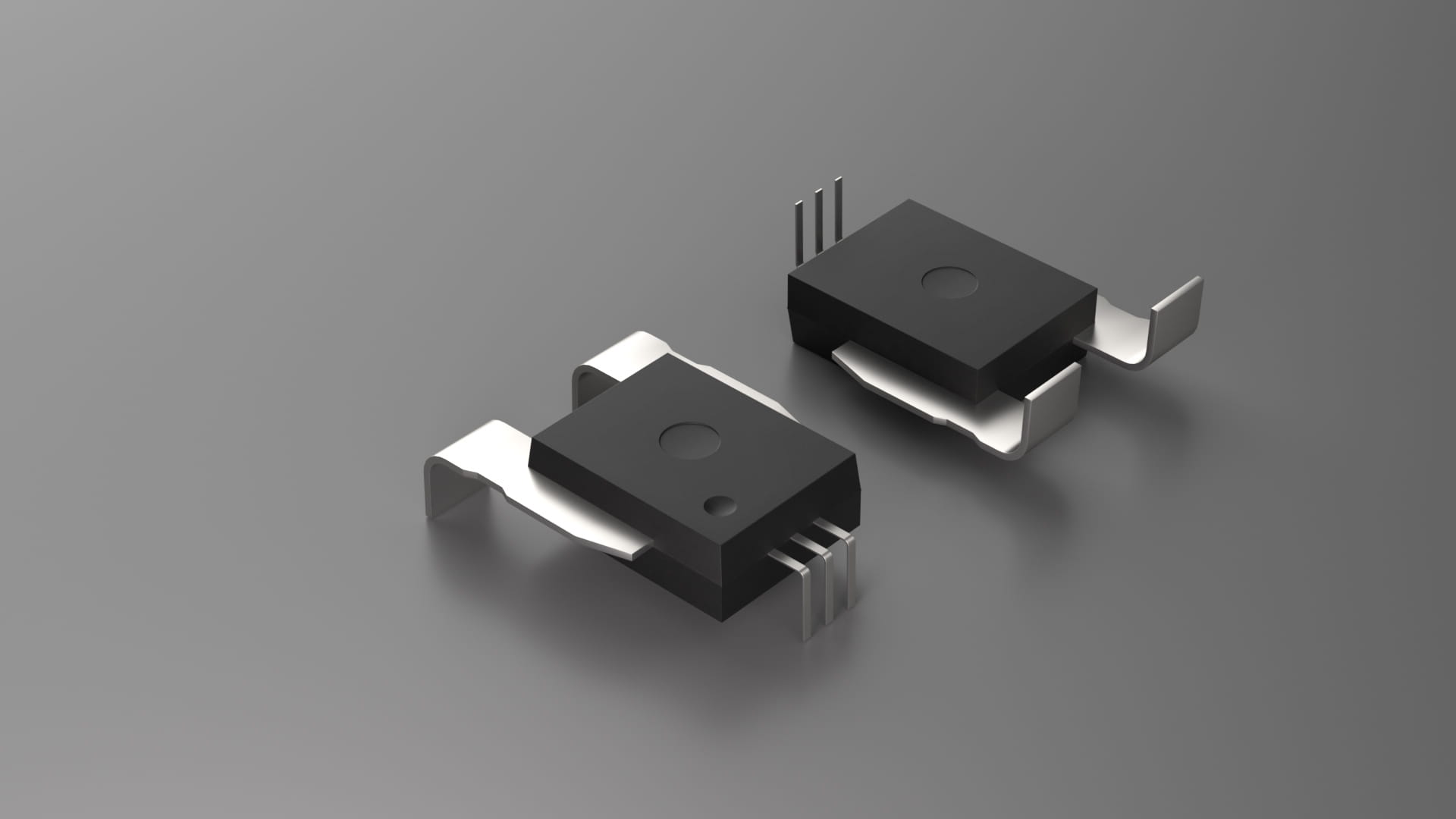
|
In-line/SMD | 3.3/5 | ±50/±100/±150/±200 | 0.5% | 4800 | 250K | 1.5 | -40~125 | 0.1 | PFF/PSS/SMT |
| GC1866 |

|
SMD | 3.3/5 | ±12/±20/±30/±40/±50 /±65 | 1% | 3500 | 250K | 1.8 | -40~125 | 0.9 | SOIC-16 |
| GC1868 |
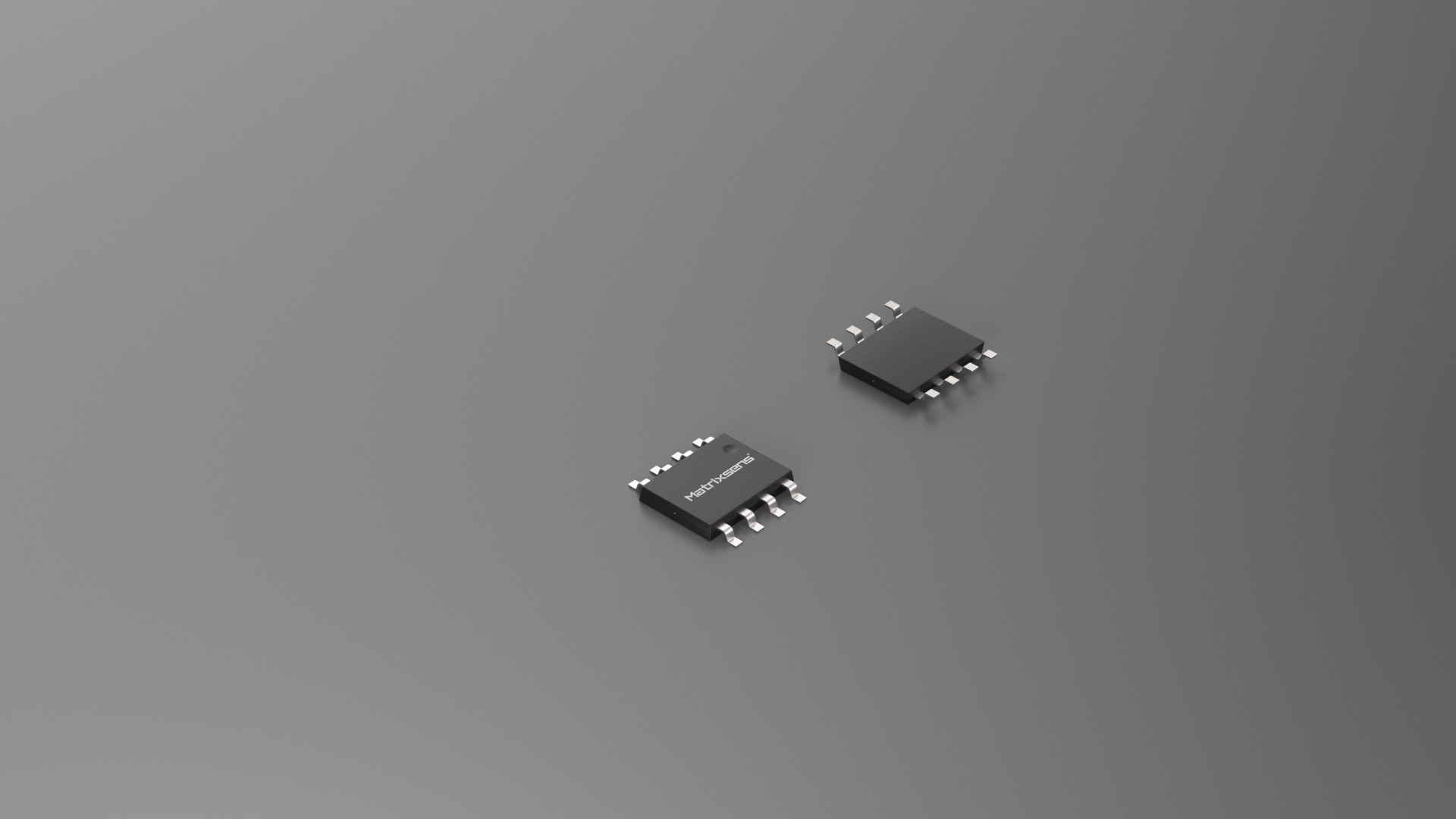
|
SMD | 3.3/5 | ±10/±20/±30/±40/±50 | 1% | 3000 | 250K | 1.8 | -40~125 | 1.2 | SOIC-8 |
| GC1860 |
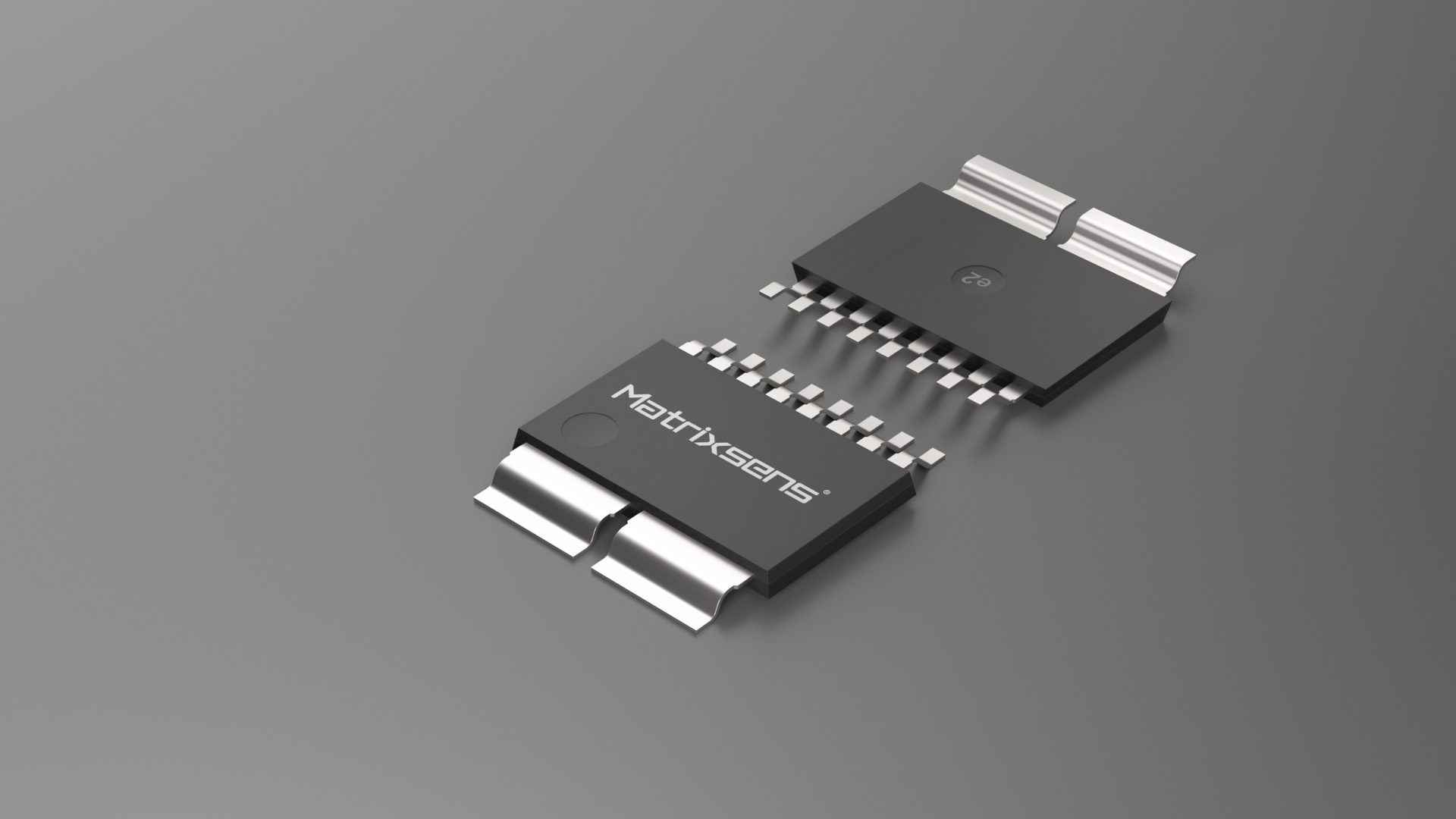
|
SMD | 3.3/5 | ±10/±20/±30/±40/ ±50/±100 | 1% | 3000 | 250K | 1.8 | -40~125 | 0.3 | SOIC-16 compatible package |


